Spring Actuator란?
DB 연결 및 애플리케이션의 성능 상태를 모니터링할 수 있는 기능이다. 그라파나 등이랑도 함께 사용할 수 있다고 한다.
주로 health check 용도의 endpoint로 많이 사용된다.
사용 방법
아래의 의존성만 추가해주면 /actuator로 접속하면 모니터링 된 내용들을 볼 수 있다.
# build.gradle
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-actuator'
}/actuator/health에 접속하면 아래와 같이 “UP”으로 서버가 살아있음을 나타내고 있는데, “components”들을 보면 어떤 것들을 헬스 체크를 하고 최종적으로 해당 서버가 살아있음을 나타내는지 보여준다.
기본 설정만 되어있으면 status만 나타나 있지만 application.properties에 management.endpoint.health.show-details: *always* 설정을 추가 해주면 세부 정보를 같이 볼 수 있다.
// http://localhost:8080/actuator/health
{
"status": "UP",
"components": {
"db": {
"status": "UP",
"details": {
"database": "MySQL",
"validationQuery": "isValid()"
}
},
"diskSpace": {
"status": "UP",
"details": {
"total": DISK_TOTAL_SIZE,
"free": DISK_FREE_SIZE,
"threshold": THRESHOLD,
"path": "/Users/Grass-Diary-Server/.",
"exists": true
}
},
"ping": {
"status": "UP"
}
}
}
기타 모니터링 정보는 아래의 PATH에서 볼 수 있다.
| 번호 | 엔드포인트 | 설명 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | self (/actuator) |
Actuator의 루트 엔드포인트, 현재 엔드포인트 목록 반환 |
| 2 | beans (/actuator/beans) |
애플리케이션 컨텍스트에 등록된 빈 목록과 의존 관계 확인 |
| 3 | caches (/actuator/caches) |
애플리케이션에서 사용 중인 캐시 조회 |
| 4 | caches-cache (/actuator/caches/{cache}) |
특정 캐시를 조회, 캐시 이름으로 필터링 가능 |
| 5 | health (/actuator/health) |
애플리케이션 상태(DB 연결, 디스크 공간 등) 확인 |
| 6 | health-path (/actuator/health/{*path}) |
특정 구성 요소(DB, 메시징 시스템 등)의 상태를 세부적으로 체크 |
| 7 | info (/actuator/info) |
애플리케이션 커스텀 정보 제공 (버전, 빌드 시간 등) |
| 8 | conditions (/actuator/conditions) |
자동 구성 상태 및 빈이 생성된 조건 확인 |
| 9 | configprops (/actuator/configprops) |
애플리케이션의 모든 구성 속성 반환 |
| 10 | configprops-prefix (/actuator/configprops/{prefix}) |
특정 접두사로 시작하는 설정 속성만 조회 |
| 11 | env (/actuator/env) |
환경 변수, 시스템 프로퍼티 및 설정 속성 반환 |
| 12 | env-toMatch (/actuator/env/{toMatch}) |
특정 환경 변수를 필터링하여 조회 |
| 13 | loggers (/actuator/loggers) |
로깅 설정을 조회 및 로그 레벨 변경 가능 |
| 14 | loggers-name (/actuator/loggers/{name}) |
특정 로거의 로그 레벨 조회 및 수정 가능 |
| 15 | heapdump (/actuator/heapdump) |
힙 덤프 생성 및 다운로드 가능, 메모리 문제 디버깅 |
| 16 | threaddump (/actuator/threaddump) |
스레드 덤프 반환, 스레드 상태 및 성능 문제 진단 |
| 17 | metrics-requiredMetricName (/actuator/metrics/{requiredMetricName}) |
특정 메트릭(jvm.memory.used 등)의 값을 조회 |
| 18 | metrics (/actuator/metrics) |
애플리케이션 성능 및 상태 메트릭 제공 (CPU, 메모리, 요청 시간 등) |
| 19 | scheduledtasks (/actuator/scheduledtasks) |
애플리케이션에 등록된 스케줄된 작업 정보 제공 |
| 20 | mappings (/actuator/mappings) |
모든 HTTP 요청 매핑 정보 확인, 각 컨트롤러와 메서드의 URL 매핑 제공 |
예를 들어 서버 내 요청 정보들도 볼 수 있는데, 내역은 아래와 같다.
// http://localhost:8080/actuator/metrics/http.server.requests
{
"name": "http.server.requests",
"description": null,
"baseUnit": "seconds",
"measurements": [
{ // 19개 요청이 처리됨
"statistic": "COUNT",
"value": 19.0
},
{ // 모든 요청이 처리되는 데 걸리는 시간 -> COUNT로 나누면 평균 처리 시간
"statistic": "TOTAL_TIME",
"value": 0.5087143350000001
},
{ // 가장 오래 걸린 처리 시간
"statistic": "MAX",
"value": 0.020212125
}
],
"availableTags": [
{
"tag": "exception", // 요청 처리 중 발생한 예외
"values": [
"none"
]
},
{
"tag": "method", // HTTP 요청 메서드
"values": [
"GET"
]
},
{
"tag": "error",
"values": [
"none"
]
},
{
"tag": "uri", // 요청이 들어온 URI 목록
"values": [
"/actuator/caches",
"/actuator",
"/actuator/beans",
"/actuator/info",
"/actuator/health",
"UNKNOWN", // 알 수 없는 경로에 대한 요청
"/actuator/loggers",
"/actuator/mappings",
"/actuator/metrics",
"/actuator/conditions",
"/actuator/env"
]
},
{
"tag": "outcome", // 요청 처리 결과
"values": [
"CLIENT_ERROR",
"SUCCESS",
"SERVER_ERROR"
]
},
{
"tag": "status", // 요청 처리 결과의 HTTP 상태 코드
"values": [
"500",
"401",
"200"
]
}
]
}
모니터링으로 사용하기 때문에 보안에 매우 신경 써줘야 하는데, 특히 env 만을 모아서 볼 수 있는 페이지도 있기 때문에 조심해야 한다.
Actuator의 보안을 신경쓴다면 아래의 우아한 테크 블로그를 참고해보자.
- Actuator 안전하게 사용하기 - 우아한 기술 블로그
우아한 기술 블로그에서 추천하는 보안대책들이 모두 반영된 application.properties 이다.
# Actuator 보안 설정 샘플
# 1. Endpoint all disable
management.endpoints.enabled-by-default = false
# 2. Enable specific endpoints
management.endpoint.info.enabled = true
management.endpoint.health.enabled = true
# 3. Exclude all endpoint for JMX and Expose specific endpoints
management.endpoints.jmx.exposure.exclude = *
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include = info, health
# 4. Use other port for Actuator
management.server.port = [포트번호]
# 5. Change Actuator Default path
management.endpoints.web.base-path = [/변경된 경로]
참고로 Intellij를 사용하면 아래와 같이 Bean의 Mapping도 볼 수 있다! (신기하다)
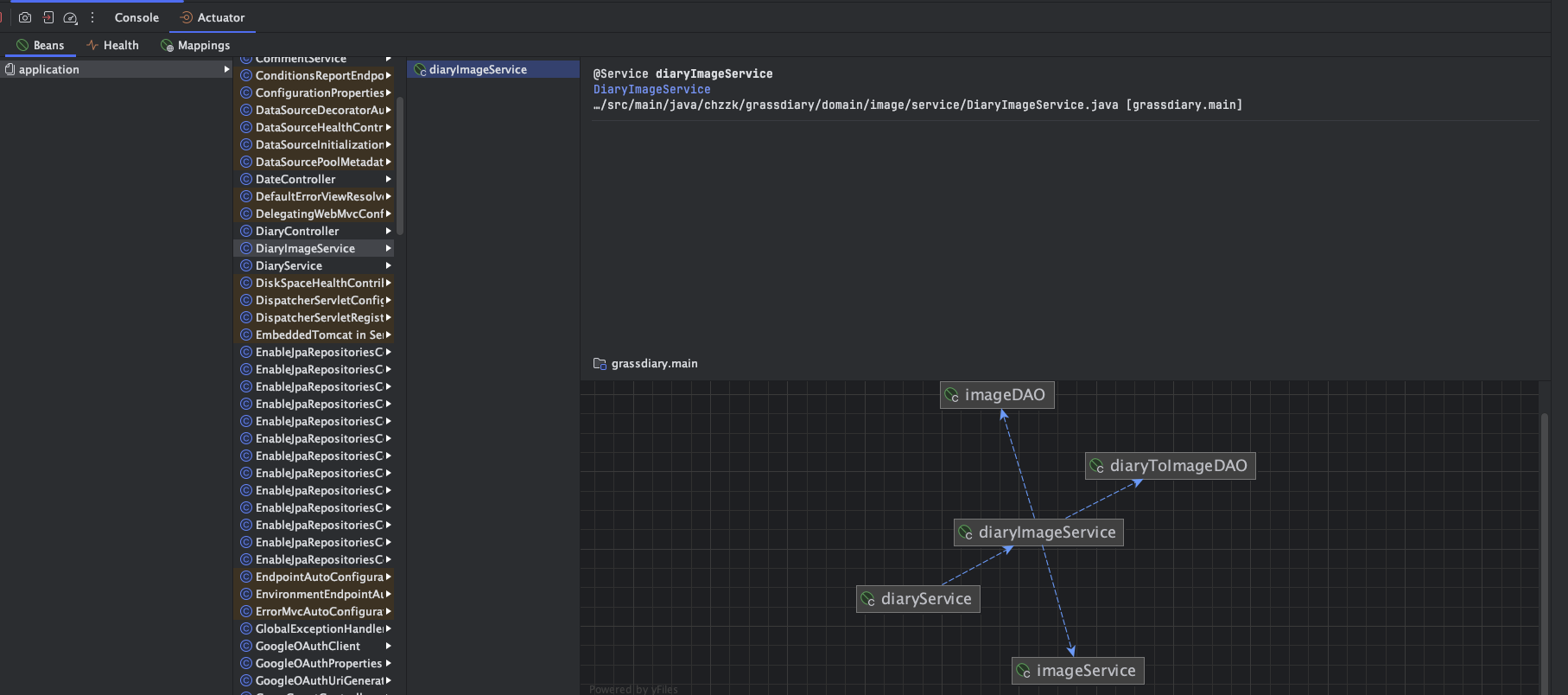
그라파나 등 모니터링 툴이랑도 함께 사용 해봐야겠다.
'알아두면 좋은 개발 지식 > Java & Spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Spring에서 동시성 이슈 해결 방법(MySQL, Redis 이용하기) (1) | 2024.09.25 |
|---|---|
| [Spring] Spring Security '인증' 과정 (1) | 2024.09.13 |
| [Java 16] 레코드(record)를 알아보자 (0) | 2024.04.13 |
| [Java] JVM의 Garbage Collector (0) | 2024.04.13 |
| 일급 컬렉션(First Class Collection)을 사용하는 이유 (0) | 2024.04.13 |

